Quick Navigation
- What is the placenta for?
- Placentophagy – A Common Practice In The Animal Kingdom
- Getting Rid Of The Smell
- Even Herbivores Instinctively Eat The Meat-like Placenta
- Reducing Pain In Labor And Maternal Behavior
- Regaining Lost Nutrients
- Increase Milk Production
- Even Our Domesticated Pets Eat The Placenta
- Conclusion:
Animals eat their placenta after giving birth to their babies, and this is just one of their many interesting instincts, knowledge, senses, and capabilities.
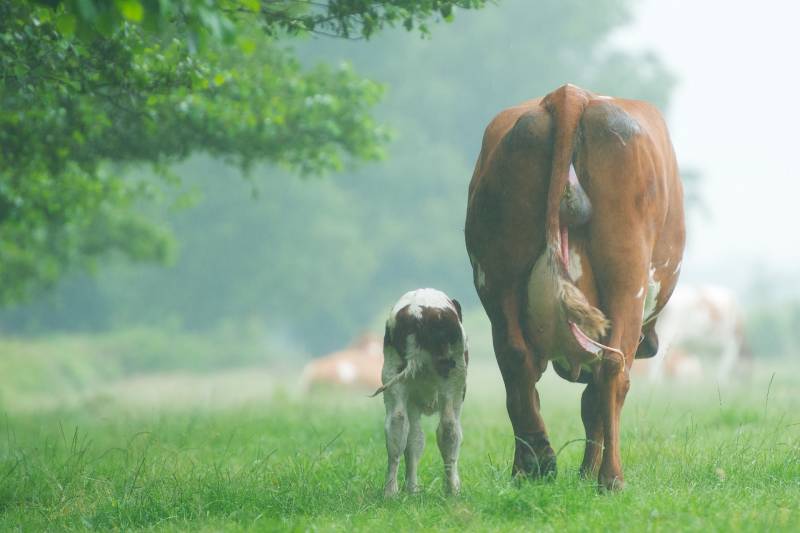

We know that warm-blooded mammals are found in every major habitat worldwide and that the females give birth to live young.
After giving birth, they also eat the placenta and suckle their young.
We’ll examine why animals do this and why it’s just one of their unusual habits.
What is the placenta for?
According to this study, the placenta facilitates fetal development and survival.
It is also an organ through which mothers and fetuses exchange gases, nutrients, and respiratory wastes.
Placentophagy – A Common Practice In The Animal Kingdom
Eating the placenta is referred to as placentophagy, a widespread practice in the animal kingdom.
Researchers believe that there are a few reasons why animals eat their placenta, and these include:
- To reduce the evidence of birth having taken place.
The female parent consuming the placenta ensures that all birthing aromas are eliminated.
This ensures that predators don’t come snooping around. - Hygiene.
We’ve all witnessed domestic and wild animals grooming themselves and others in their pride or troop.
Animals consume the placenta and feces of the young to keep things clean in the area where they will spend their first few weeks. - To replenish lost nutrients during pregnancy, labor, and birth.
- To acquire additional hormones.
There are protein and peptide hormones in the placenta of various species, and it is thought they will affect the mother – prepare her for the support of her young.
Placental mammals cover many species, from rats to elephants to dogs and cats.
Placental mammals all bear live young.
Their babies are nourished in the mother’s uterus through the placenta.
During birth, the placenta is often pushed out after the baby.
The mother then licks and eats the amniotic sac’s remains while licking and cleaning the newborn and then turns to consume the placenta.
Getting Rid Of The Smell
You could say that the most apparent reason for animals consuming the placenta after birth is to keep predators at bay.
Predators such as leopards and lions are attracted to birthing sites because of fetal tissue and blood scent.
So mother mammals ingest the afterbirth to eliminate the evidence of birth and steer predators away from looking for defenseless newborns.
Even Herbivores Instinctively Eat The Meat-like Placenta
The fascinating thing about animals eating the placenta is that you get carnivores, herbivores, and omnivores in the animal kingdom.
Herbivorous animals are those that feed on grass, plants, and fruits.
They also regurgitate their food.
Interestingly, some herbivore animals, such as goats and zebras, don’t recoil from eating the placenta, even as herbivores.
After all, a placenta is an internal organ filled with fluid and veins.
It is essentially spongy meat and protein, playing an essential role in helping the fetus to develop.
We can understand carnivores and omnivores eating the placenta but a herbivore?
That’s amazing with animals – they instinctively know what to do.
A herbivore will turn away from its instinct to only feed on plants.
This is when it will consume a piece of meat to clean up the ‘mess’ of the birth and hide all smells indicating that the birth occurred.
Omnivore Monkeys Eat The Placenta Too
Many people have observed monkeys for months to observe their behavior with birthing.
While most monkeys give birth at night, after decades of observation, researchers have seen monkeys giving birth during the day.
This particular monkey, a wild golden snub-nosed monkey, had a ‘midwife’ to assist her.
As the baby’s crown appeared, the midwife tried to assist by pulling the baby monkey out.
She then attended to the mother afterward and assisted her by cleaning the baby.
After the mother gave birth, she cut the umbilical cord and spent 5 minutes eating the placenta.
Reducing Pain In Labor And Maternal Behavior
Some medical experts have spent decades researching why animals like rats consume the placenta.
They have discovered that the placenta contains compounds that allow those ingesting it to have better pain tolerance.
Natural opioids are produced in labor to reduce pain.
Research teaches us that ingestion of amniotic fluid and the placenta impacts the pain and pain tolerance a pregnant rat endures.
This is put down to the rise of these naturally occurring endogenous opioids.
With the ingestion of the placenta, there is an increase in the opioid effect.
Placentophagia has been studied in rats, and one finding is that the consumption of afterbirth also increases maternal behavior in rats.
In addition to increasing these maternal tendencies of mother rats, it has been seen that placentophagia also encourages alloparenting behavior.
This is where other rats also perform the role of parents towards younger rats.
Regaining Lost Nutrients
It is also thought that animals eat their placenta as they instinctively believe they are regaining all the nutrients they lost during the birthing process.
Some people also believe that eating the placenta encourages the mother-baby bonding process.

This hypothesis has stirred interest in humans to consider placentophagy.
There are some critics, however, who say that the practice could be harmful to humans.
The placenta is a nutritious piece of protein, and after all the effort of carrying young and giving birth, the placenta replaces lost nutrients.
It helps the mother prepare to nurse the hungry babies.
The placentas are nourishing and full of vitamins, minerals, and protein.
Some animals are in labor for a long time, and during labor, when the animals are stressed, they don’t eat.
After giving birth, most animals won’t leave their young for a day or two.
Increase Milk Production
Consuming the placenta after birth will nourish the mother and help with milk production.
In the study of Blank and Friesen, rats that consumed their placenta after giving birth increased the concentration of prolactin, a hormone that stimulates milk production.
Even Our Domesticated Pets Eat The Placenta
Many of us have had the privilege of owning a dog as a pet.
We’ve stood in amazement at how the female instinctively knows what to do with the puppies once they are born.
They can often teach humans a thing or two about caring for newborns.
When a domesticated female dog gives birth, the mother dog knows what to do.
After the birth, the mother dog frees each puppy from the sac.
She then does an excellent job of licking each puppy clean and freeing each one from the umbilical cord.
She may consume the placenta of each puppy.
Even though a domesticated dog no longer lives in the wild, it eats the placenta to clean up the area and remove birthing scents.
She wants to ensure that the birth’s scent, just like she would in the wild, do not attract predators.
This comes from when dogs were still wild and lived in dens.
Not only does the mother dog eat the pup’s placenta, but she would also keep the den spotlessly clean by eating the pup’s feces.
She does all these things to ensure that predators never get a whiff that there is a meal to be had close by.
Domesticated dogs, too, will eat the puppies’ feces to keep their basket clean.
Conclusion:
Many animals lick the amniotic fluid during labor and then consume the placenta.
This activity has been documented by many researchers who have studied placentophagy in many species of female mammals.
Even with multi-births, the mother animal will diligently eat the placenta of each young.
There are a few theories as to why mammals engage in placentophagy.
We’ve looked at just a few, and each makes perfect sense.
Animals are unique, and they’ve discovered on their own, without being taught, the many advantages of placental consumption and its many benefits to their young.

A passionate content creator on pet behavior, nutrition choices, and health, Mike is an experienced pet expert. He has been writing on multiple websites to compensate for his passion for cats. Mike grieves around plenty of pets in his parents’ house. At the start of his career, he had a sturdy intention to be a part of pet care by any means.
With his affiliation to Purrfect n’ Pawesome, he found a way to satiate his craving to participate in pet health, wellness, and behavior analysis. He has been a significant part of our team and a major contributor in equipping our site with useful, authentic, and research-backed articles.
“I love pets as much as I love to travel to explore multiple places and lifestyles. I have been attached to this pawsome platform for many years, and my experience regarding pets has enhanced significantly by using various devices to write articles. I believe in writing my thoughts and experiences, so I try to write down the experience and learnings for my readers no matter where I am and what my mood is.”